Cryptography Introduction (with .NET code example)¶
Cryptography is the core part of security, this blog introduces the basic concepts in cryptography and uses .NET as code example.
Randomness¶
System.Random and its problems
System.Random is a pseudo random number generator
A seed value is passed into the constructor
The seed value should be different each time
System.Random is deterministic and predictable
Solution is to use RNGCryptoServiceProvider instead.
public static byte[] GenerateRandomNumber(int length)
{
using (var randomNumberGenerator = new RNGCryptoServiceProvider())
{
var randomNumber = new byte[length];
randomNumberGenerator.GetBytes((randomNumber));
return randomNumber;
}
Hashing¶
What Is Hashing?
It is easy to compute the hash value for any given message
It is infeasible to generate a message that has a given hash
It is infeasible to modify a message without changing the hash
It is infeasible to find two different messages with the same hash
Hash algorithm
MD5
SHA-1
SHA-256
SHA-512
Hashing is one way operation, while encryption is two way operation.
MD5
Designed by Ron Rivest in 1991 to replace MD4
Produces a 128 bit (16 byte) hash value
Commonly used to verify file integrity
First collision resistance flaw found in 1996
Recommendation was to move over to the Secure Hash Family
Further collision resistance problems found in 2004
Still needed when integrating with legacy systems
SHA1 SHA2: SHA256, SHA512 SHA3: not supported in .net so far (2015)
public class HashData
{
public static byte[] ComputeHashSha1(byte[] toBeHashed)
{
using (var sha1 = SHA1.Create())
{
return sha1.ComputeHash(toBeHashed);
}
}
public static byte[] ComputeHashSha256(byte[] toBeHashed)
{
using (var sha256 = SHA256.Create())
{
return sha256.ComputeHash(toBeHashed);
}
}
public static byte[] ComputeHashSha512(byte[] toBeHashed)
{
using (var sha512 = SHA512.Create())
{
return sha512.ComputeHash(toBeHashed);
}
}
public static byte[] ComputeHashMd5(byte[] toBeHashed)
{
using (var md5 = MD5.Create())
{
return md5.ComputeHash(toBeHashed);
}
}
}
Hash algorithm with key¶
Hashed Message Authentication Codes
public class Hmac
{
private const int KeySize = 32;
public static byte[] GenerateRandomKey()
{
using (var randomNumberGenerator = new RNGCryptoServiceProvider())
{
var randomNumber = new byte[KeySize];
randomNumberGenerator.GetBytes((randomNumber));
return randomNumber;
}
}
public static byte[] ComputeHmacsha256(byte[] toBeHashed, byte[] key)
{
using (var hmac = new HMACSHA256(key))
{
return hmac.ComputeHash(toBeHashed);
}
}
public static byte[] ComputeHmacsha1(byte[] toBeHashed, byte[] key)
{
using (var hmac = new HMACSHA1(key))
{
return hmac.ComputeHash(toBeHashed);
}
}
}
Store Password¶
Store password: store plain text and encrypted password is not good idea. Store hash since it cannot be reversed.
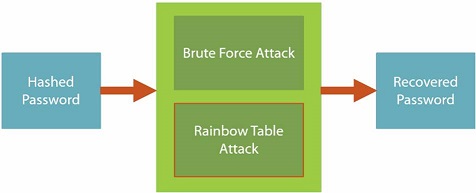
Rainbow table contains pre-computed hash to speed up the attack. Add salt will make brute force and rainbow table attack ineffective.
public class Hash
{
public static byte[] GenerateSalt()
{
const int saltLength = 32;
using (var randomNumberGenerator = new RNGCryptoServiceProvider())
{
var randomNumber = new byte[saltLength];
randomNumberGenerator.GetBytes(randomNumber);
return randomNumber;
}
}
private static byte[] Combine(byte[] first, byte[] second)
{
var ret = new byte[first.Length + second.Length];
Buffer.BlockCopy(first, 0, ret, 0, first.Length);
Buffer.BlockCopy(second, 0, ret, first.Length, second.Length);
return ret;
}
public static byte[] HashPasswordWithSalt(byte[] toBeHashed, byte[] salt)
{
using (var sha256 = SHA256.Create())
{
return sha256.ComputeHash(Combine(toBeHashed, salt));
}
}
}
PBKDF¶
The salt does not have to be secret, which can be stored in the database. If the computational power become bigger, it still has risk just by adding salt.
Password Based Key Derivation Functions
Password Based Key Derivation Function (PBKDF2)
RSA Public Key Cryptographic Standards (PKCS #5 Version 2.0)
Internet Engineering Task Force RFC 2898 Specification
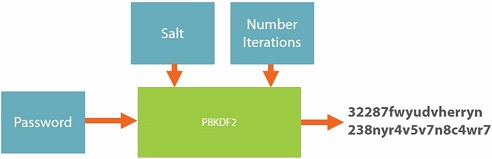
Number Iteration: numbers of hashing function, which can scale with increasing computational power
Good default is 50,000 iterations
Balance number of iterations with acceptable performance
Ideally double number of iterations every 2 years
public class Pbkdf2
{
public static byte[] GenerateSalt()
{
using (var randomNumberGenerator = new RNGCryptoServiceProvider())
{
var randomNumber = new byte[32];
randomNumberGenerator.GetBytes(randomNumber);
return randomNumber;
}
}
public static byte[] HashPassword(byte[] toBeHashed, byte[] salt, int numberOfRounds)
{
using (var rfc2898 = new Rfc2898DeriveBytes(toBeHashed, salt, numberOfRounds))
{
return rfc2898.GetBytes(32);
}
}
}
Symmetric Algorithm¶
Advantages of symmetric encryption:
Extremely secure
Relatively fast
Disadvantage:
Key sharing
More damage if compromised
A new variant designed called Triple DES, which is a simple way to increase key size without redesigning a new cipher. Many former DES users now use Triple DES. Triple DES involved applying DES three times with 2 or 3 different keys. Triple DES was regarded as adequately secure, although it is quite slow.
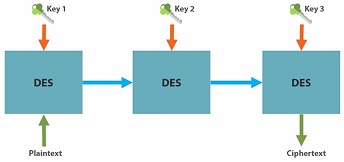
CLR uses a stream oriented design for cryptography. Core of the design is CryptoStream.
public byte[] Encrypt(byte[] dataToEncrypt, byte[] key, byte[] iv)
{
using (var des = new DESCryptoServiceProvider())
{
des.Mode = CipherMode.CBC;
des.Padding = PaddingMode.PKCS7;
des.Key = key;
des.IV = iv;
using (var memoryStream = new MemoryStream())
{
var cryptoStream = new CryptoStream(memoryStream, des.CreateEncryptor(),
CryptoStreamMode.Write);
cryptoStream.Write(dataToEncrypt, 0, dataToEncrypt.Length);
cryptoStream.FlushFinalBlock();
return memoryStream.ToArray();
}
}
}
public byte[] Decrypt(byte[] dataToDecrypt, byte[] key, byte[] iv)
{
using (var des = new DESCryptoServiceProvider())
{
des.Mode = CipherMode.CBC;
des.Padding = PaddingMode.PKCS7;
des.Key = key;
des.IV = iv;
using (var memoryStream = new MemoryStream())
{
var cryptoStream = new CryptoStream(memoryStream, des.CreateDecryptor(),
CryptoStreamMode.Write);
cryptoStream.Write(dataToDecrypt, 0, dataToDecrypt.Length);
cryptoStream.FlushFinalBlock();
return memoryStream.ToArray();
}
}
}
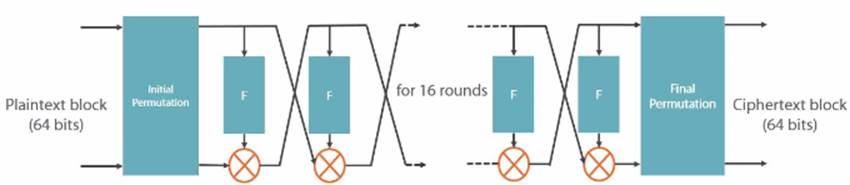
How does DES and Triple DES work?
DES is a block cipher that transforms plaintext into ciphertext
DES uses a block size of 64 bits
Uses a 64 bits key only 56 bits are used by the algorithm
Supports different modes of operation
The history of AES
Unlike DES, AES does not use a Feistel network
Uses 128 bit block size and 128, 192 or 256 bit keys
Based on a design known as a substitution - permutation network
How Secure is AES against brute force attack?
Key Size |
Possible Combinations |
1 bit |
2 |
2 bit |
4 |
4 bit |
16 |
8 bit |
256 |
16 bit |
65536 |
32 bit |
4.2 x 10 9 |
56 bit (DES) |
7.2 x 10 16 |
64 bit |
1.8 x 10 19 |
128 bit (AES) |
3.4 x 10 38 |
192 bit (AES) |
6.2 x 10 57 |
256 bit (AES) |
1.1 x 10 77 |
.NET Framework libraries for symmetric algorithm:
DESCryptoServiceProvider
TripleDESCryptoServiceProvider
AESCryptoServiceProvider
Asymmetric Encryption¶
RSA has 3 key sizes:
1024 bit key
2048 bit key
4096 bit key
Some facts about asymmetric encryption algorithm:
Public and private keys are based on prime numbers
Factoring a number back into constituent prime numbers is hard
RSA encryption and decryption is a mathematical operation based on modular math
private RSAParameters _publicKey;
private RSAParameters _privateKey;
public void AssignNewKey()
{
using (var rsa = new RSACryptoServiceProvider(2048))
{
rsa.PersistKeyInCsp = false;
this._publicKey = rsa.ExportParameters(false);
this._privateKey = rsa.ExportParameters(true);
}
}
It is not recommended to store private key on your file system, try to use key container
public void AssignNewKeyWithContainer()
{
const int ProviderRsaFull = 1;
CspParameters cspParameters = new CspParameters(ProviderRsaFull)
{
KeyContainerName = "MyContainerName",
Flags = CspProviderFlags
.UseMachineKeyStore,
ProviderName =
"Microsoft Strong Cryptographic Provider"
};
var rsa = new RSACryptoServiceProvider(cspParameters) { PersistKeyInCsp = true };
}
public void DeleteKeyInCsp()
{
var cspParams = new CspParameters { KeyContainerName = "MyContainerName" };
var rsa = new RSACryptoServiceProvider(cspParams) { PersistKeyInCsp = false };
rsa.Clear();
}
How to encrypt and decrypt data
public byte[] EncryptData(byte[] dataToEncrypt)
{
byte[] cipherbytes;
using (var rsa = new RSACryptoServiceProvider(2048))
{
rsa.ImportParameters(this._publicKey);
cipherbytes = rsa.Encrypt(dataToEncrypt, false);
}
return cipherbytes;
}
public byte[] DecryptData(byte[] dataToEncrypt)
{
byte[] plain;
using (var rsa = new RSACryptoServiceProvider(2048))
{
rsa.PersistKeyInCsp = false;
rsa.ImportParameters(this._privateKey);
plain = rsa.Decrypt(dataToEncrypt, true);
}
return plain;
}
public byte[] DecryptDataWithCsp(byte[] dataToDecrypt)
{
byte[] plain;
var cspParams = new CspParameters { KeyContainerName = "MyContainerName" };
using (var rsa = new RSACryptoServiceProvider(2048, cspParams))
{
plain = rsa.Decrypt(dataToDecrypt, false);
}
return plain;
}
Digital Signatures¶
Claiming authenticity of a message
Digital signatures give both authentication and non-repudiation
Based on asymmetric cryptography
Digital signatures consist of: 1. Public and private key generation; 2. Signing algorithm using the private key
Verification algorithm using the public key
Difference between normal asymmetric encryption and digital sign:
normal asymmetric encryption: sender use public key to encrypt data, and receiver uses private key to decrypt data
digital sign: sender use private key to generate digital sign, and receiver uses public key to verify the digital sign
Public Key |
Private Key |
|
Encryption (RSA) |
Encrypt |
Decrypt |
Digital Signatures |
Verify Signature |
Sign Message |
Digital Signature in .NET use 3 main classes
RSACryptoServiceProvider
RSAPKCS1SignatureFormatter
RSAPKCS1SignatureDeformatter
public byte[] SignData(byte[] hashOfDataToSign)
{
using (var rsa = new RSACryptoServiceProvider(2048))
{
rsa.PersistKeyInCsp = false;
rsa.ImportParameters(this._privateKey);
var rsaFormatter = new RSAPKCS1SignatureFormatter(rsa);
rsaFormatter.SetHashAlgorithm("SHA256");
return rsaFormatter.CreateSignature(hashOfDataToSign);
}
}
public bool VerifySignature(byte[] hashOfDataToSign, byte[] signature)
{
using (var rsa = new RSACryptoServiceProvider(2048))
{
rsa.ImportParameters(this._publicKey);
var rsaDeformatter = new RSAPKCS1SignatureDeformatter(rsa);
rsaDeformatter.SetHashAlgorithm("SHA256");
return rsaDeformatter.VerifySignature(hashOfDataToSign, signature);
}
}
Comparision between hashing, MAC and digital sign¶
Integrity: Can the recipient be confident that the message has not been accidentally modified?
Authentication: Can the recipient be confident that the message originates from the sender?
Non-repudiation: If the recipient passes the message and the proof to a third party, can the third party be confident that the message originated from the sender?
Cryptographic primitive Security Goal |
Hash |
MAC |
Digital signature |
|
|
|
|
Kind of keys |
none |
|
|
Secure String¶
System.String is not a secure solution, which has the following problems:
Several copies in memory
Not encrypted
Not mutable, old copied in memory
No effective way to clear out memory
Using SecureString for sensitive data
SecureString stored in encrypted memory
SecureString implements IDisposable
Create SecureString with a pointer to a char array
public static string CovertToUnsecureString(SecureString securePassword)
{
var unmanagedString = IntPtr.Zero;
try
{
unmanagedString = Marshal.SecureStringToGlobalAllocUnicode(securePassword);
return Marshal.PtrToStringUni(unmanagedString);
}
finally
{
Marshal.ZeroFreeGlobalAllocUnicode(unmanagedString);
}
}
private static SecureString ToSecureString(char[] str)
{
var secureString = new SecureString();
Array.ForEach(str, secureString.AppendChar);
return secureString;
}
private static char[] CharacterData(SecureString secureString)
{
char[] bytes;
var ptr = IntPtr.Zero;
try
{
ptr = Marshal.SecureStringToBSTR(secureString);
bytes = new char[secureString.Length];
Marshal.Copy(ptr, bytes, 0, secureString.Length);
}
finally
{
if (ptr != IntPtr.Zero)
{
Marshal.ZeroFreeBSTR(ptr);
}
}
return bytes;
}
Written by Binwei@Oslo
